Summary
In this project I made melodies in the key of C that were 8 measures long, I also broke down the melodies. I learned about music theory and the history of music.
My First HookTheory Melody
I was told to throw a bunch of notes on 8 measures.
Notes from Howard Goodall’s Melody Video
How Music Works with Howard Goodall – Melody
| Cue | Notes |
| Semitone Modes Notes Scales Music Theory Pitch Pentatonic Major Minor Diatonic Coldplay Melody Dorian | Everything is made up of the same 5 notes and It’s called pentatonic How high or low a note is, is called pitch Modes The minor scale is a mix of modes You can start on whatever semi note in a minor scale because it can cope Major and minor scales are compatible |
Summary: In this video, I learned about major and minor scales, modes, notes, scales, pitch, diatonic music, tones, and semitones.
Melody Composition Terms and Definitions

- The terms and definitions below are from the Basic Concepts of Music Theory podcast by Jamie Henke at the University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Her Basic Concepts of Music Theory video on YouTube
- Theme: A long, flowing melodic idea.
- Motive: A short, rhythmic idea (Beethoven’s 5th).
- Period: 8-12 measures or a musical sentence.
- Phrase: Usually 4 measures.
- Antecedent (Question) Phrase: First 4 measures of a period.
- Consequent (Answer) Phrase: Second 4 measures of a period.
- Scale Degrees (C Major Scale)
- Tonic: C (1 , 8) – Stability and resolve.
- Supertonic, Mediant, Submediant: D, E, A (2 , 3 , 6) – Moderate tension, useful for transitions and carrying on an idea.
- Subdominant, Dominant, Leading Tone: F, G, B (4 , 5 , 7) – Causes the most tension, leads to the tonic.
- Steps: Any movement using half or whole steps.
- Leaps: Any movement using intervals larger than a whole step.
- Conjunct motion: Melody is built primarily out of steps.
- Disjunct motion: Melody is built primarily out of leaps.
- Repetition: Repeated material (i.e. motive) used to create a link between two phrases of the period.
- Contrast: Two phrases that contain contrasting material to create tension and interest.
- Variation: Halfway between contrast and repetition. The two phrases include some recognizable material and some varied material (i.e. taking ideas up an octave).
One of My Favorite Melodies
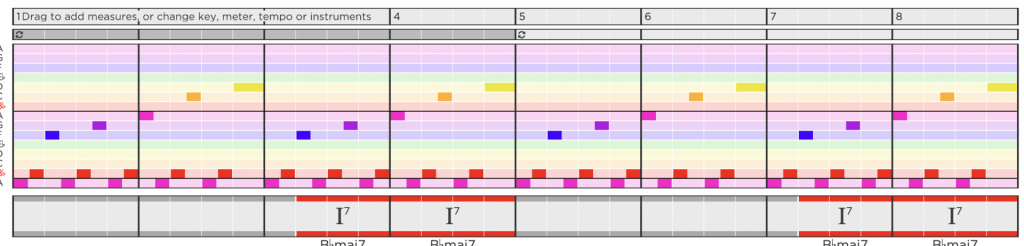
This melody is in B-flat, the tonic note is B flat, the dominant note is F and the leading note is an A. I noticed that the melody repeats its self.
My Second HookTheory Melody
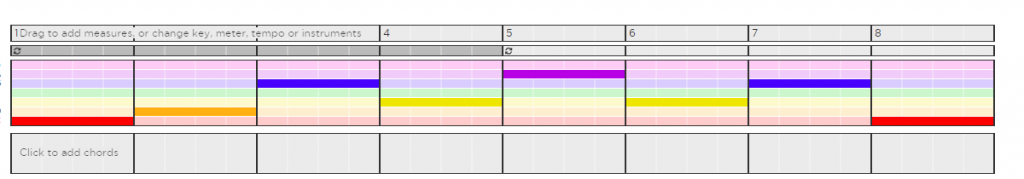
I made a slow melody with rising and descending notes. It is in the key of C. The tonic notes are C. I used G to build tension and it is dominant. I made use of mediant and submediant notes on bars 4 and 5, I used an E on bar 4 as a mediant and I used an A on bar 5 as a submediant. I made use of variation in all measures. I used retrograde in measures 6, 7, and 8.
What I Learned & Problems I Solved
- I learned about music theory examples being tonics, tension notes, melody…etc
- I learned how to use HookPad
- I learned about the history of music
- One problem I overcame was trying to understand the music theory it was very frustrating.
Resources
- Assessment a Feedback
- General Music Composition Rubric (Google Doc)
- Period Melody Composition Rubric (PDF)
- Hook Theory Tools and Tutorials
- Music Theory
- Mr. Le Duc’s Key of C Major Notes and Chords Chart (PDF)
- How Music Works with Howard Goodall – Melody
- Melody defined at Wikipedia
- iTunesU – Basic Concepts of Music Theory by Jamie Henke at University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Her Basic Concepts of Music Theory video on YouTube
- https://www.youtube.com/embed/rl-V2IsUprQ
- Michael New
- Art of Composing
- Free MIDI files midiworld.com/files/
- MIDI file of Beethoven’s Ode to Joy from his 9th symphony
- Coldplay Talk sample midi file
- MIDI and Music Notation Editors
- onlinesequencer.net – online
- flat.io – online
- noteflight.com – online
- MuseScore downloadable program
- GarageBand
- Melody Research, Analysis, and Recording Project Feedback Form (PDF)